3.6. Configuring Cluster Daemons
The Red Hat Cluster Manager provides the following daemons to monitor cluster operation:
cluquorumd — Quorum daemon
clusvcmgrd — Service manager daemon
clurmtabd — Synchronizes NFS mount entries in /var/lib/nfs/rmtab with a private copy on a service's mount point
clulockd — Global lock manager (the only client of this daemon is clusvcmgrd)
clumembd — Membership daemon
Each of these daemons can be individually configured using the Cluster Configuration Tool. To access the Cluster Daemon Properties dialog box, choose Cluster => Daemon Properties.
The following sections explain how to configure cluster daemon properties. However, note that the default values are applicable to most configurations and do not need to be changed.
3.6.1. Configuring clumembd
On each cluster system, the clumembd daemon issues heartbeats (pings) across the point-to-point Ethernet lines to which the cluster members are connected.
 | Note |
|---|---|
You can enable both broadcast heartbeating and multicast heartbeating, but at least one of these features must be used. Multicast heartbeating over a channel-bonded Ethernet interface provides good fault tolerance and is recommended for availability. |
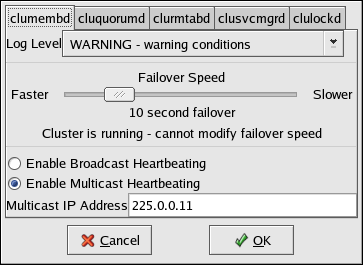
You can specify the following properties for the clumembd daemon:
Log Level — Determines the level of event messages that get logged to the cluster log file (by default /var/log/messages). Choose the appropriate logging level from the menu. Refer to Section 3.12 Configuring syslogd Event Logging for more information.
Failover Speed—Determines the number of seconds that the cluster service waits before shutting down a non-responding member (that is, a member from which no heartbeat is detected). To set the failover speed, drag the slider bar. The default failover speed is 10 seconds.

Note Setting a faster failover speed increases the likelihood of false shutdowns.
Heartbeating — Enable Broadcast Heartbeating or Enable Multicast Heartbeating by clicking the corresponding radio button. Broadcast heartbeating specifies that the broadcast IP address is to be used by the clumembd daemon when emitting heartbeats.
By default, the clumembd is configured to emit heartbeats via multicast. Multicast uses the network interface associated with the member's hostname for transmission of heartbeats.
Multicast IP Address — Specifies the IP address to be used by the clumembd daemon over the multicast channel. This field is not editable if Enable Broadcast Heartbeating is checked. The default multicast IP address used by the cluster is 225.0.0.11.
3.6.2. Configuring cluquorumd
In a two-member cluster without a specified tiebreaker IP address, the cluquorumd daemon periodically writes a time-stamp and system status to a specific area on the primary and shadow shared partitions. The daemon also reads the other member's timestamp and system status information from the primary shared partition or, if the primary partition is corrupted, from the shadow partition.
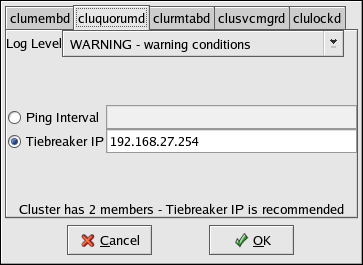
You can specify the following properties for the cluquorumd daemon:
Log Level — Determines the level of event messages that get logged to the cluster log file (by default /var/log/messages). Choose the appropriate logging level from the menu. Refer to Section 3.12 Configuring syslogd Event Logging for more information.
Ping Interval or Tiebreaker IP — Ping Interval is used for a disk-based heartbeat; specifies the number of seconds between the quorum daemon's updates to its on-disk status.
Tiebreaker IP is a network-based heartbeat used to determine quorum, which is the ability to run services. The tiebreaker IP address is only checked when the cluster has an even split in a two- or four-member cluster. This IP address should be associated with a router that, during normal operation, can be reached by all members over the Ethernet interface used by the cluster software.
3.6.3. Configuring clurmtabd
The clurmtabd daemon synchronizes NFS mount entries in /var/lib/nfs/rmtab with a private copy on a service's mount point. The clurmtabd daemon runs only when a service with NFS exports is running.
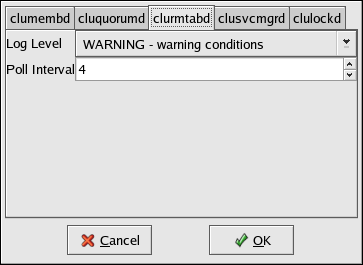
You can specify the following properties for the clurmtabd daemon:
Log Level — Determines the level of event messages that get logged to the cluster log file (by default, /var/log/messages). Choose the appropriate logging level from the menu. See Section 3.12 Configuring syslogd Event Logging for more information.
Poll Interval—Specifies the number of seconds between polling cycles to synchronize the local NFS rmtab to the cluster rmtab on shared storage.
3.6.4. Configuring the clusvcmgrd daemon
On each cluster system, the clusvcmgrd service manager daemon responds to changes in cluster membership by stopping and starting services. You might notice, at times, that more than one clusvcmgrd process is running; separate processes are spawned for start, stop, and monitoring operations.
You can specify the following properties for the clusvcmgrd daemon:
Log Level — Determines the level of event messages that get logged to the cluster log file (by default, /var/log/messages). Choose the appropriate logging level from the menu. See Section 3.12 Configuring syslogd Event Logging for more information.
3.6.5. Configuring clulockd
The clulockd daemon manages the locks on files being accessed by cluster members.
You can specify the following properties for the clulockd daemon:
Log Level — Determines the level of event messages that get logged to the cluster log file (by default, /var/log/messages). Choose the appropriate logging level from the menu. See Section 3.12 Configuring syslogd Event Logging for more information.